 Deimos
Deimos Deimos
DeimosMars II

Deimos [DEE-mos] (panic) is a moon of Mars and was named after an attendant of the Roman war god Mars. Deimos is a dark body that appears to be composed of C-type surface materials. It is similar to the C-type (blackish carbonaceous chondrite) asteroids that exist in the outer asteroid belt. Some scientists speculate that Deimos and Phobos (the other martian moon), are captured asteroids; however, other scientists present arguments counter to this theory. Both Deimos and Phobos are saturated with craters. Deimos has a smoother appearance caused by partial filling of some of its craters.

Discovered by .................................... Asaph Hall Date of discovery ...................................... 1877 Mass (kg) ........................................... 1.8e+15 Mass (Earth = 1) ................................. 3.0120e-10 Radius (km) ..................................... 7.5x6.1x5.5 Radius (Earth = 1) ............................... 1.1759e-03 Mean density (gm/cm^3) .................................. 1.7 Mean distance from Mars (km) ......................... 23,460 Rotational period (days) ............................ 1.26244 Orbital period (days) ............................... 1.26244 Mean orbital velocity (km/sec) ......................... 1.36 Orbital eccentricity ................................... 0.00 Orbital inclination ................................. 0.9-2.7° Escape Velocity (km/sec) ............................. 0.0057 Visual geometric albedo ................................ 0.07 Magnitude (Vo) ........................................ 12.40

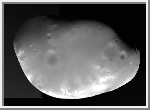
 Mosaic of Deimos
(GIF, 181K)
Mosaic of Deimos
(GIF, 181K)
Measuring 16 by 12 km (10 by 7.5 mi)
Deimos circles Mars every 30 hours. Craters of varying age dot its
surface, which is somewhat smoother than the surface of Phobos.
(Courtesy NASA/JPL)
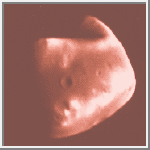 Deimos
(GIF, 13K)
Deimos
(GIF, 13K)
This image was taken by the
Viking Orbiter spacecraft in 1977.
(Courtesy NSSDC/NASA)
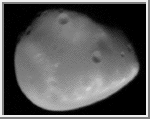 Deimos
(GIF, 50K;
JPEG, 8K)
Deimos
(GIF, 50K;
JPEG, 8K)
This image shows a slightly different view of Deimos. It was acquired
by the Viking Orbiter spacecraft.
(Credit: Calvin J. Hamilton)
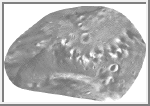 Map of Deimos
(GIF, 102K;
caption)
Map of Deimos
(GIF, 102K;
caption)
This image is a photomosaic of Deimos, the outer satellite of Mars.
The leading side faces forwards in the orbit of Deimos. The trailing
side faces backwards along the orbit. Longitude
0 is at the blunter end with the most prominent craters, and faces Mars.
As with all conformal (true shape) projections, the scale in these maps
varies, increasing from the centre to the outer edge.
(Courtesy Phil Stooke, NSSDC, and NASA)

